Introduction: The Global General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) market has been a significant player in the plastics industry, finding applications in various sectors such as packaging, electronics, construction, and automotive. In this essay, we will provide an overview of the GPPS market and analyze its expected trajectory in the next five years.
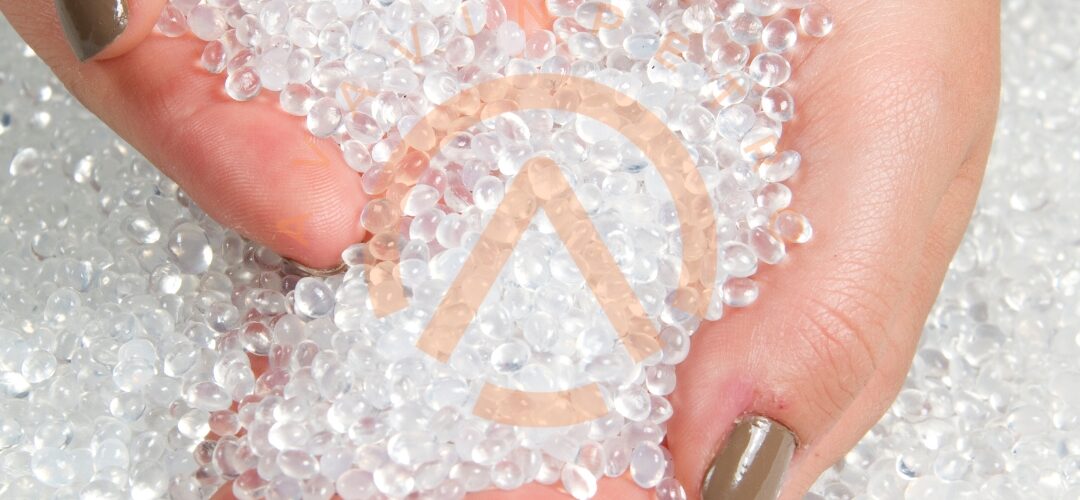
Current State of the GPPS Market: The GPPS market has witnessed steady growth in recent years, driven by its favorable properties, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. GPPS is a transparent and rigid thermoplastic that is easy to process, making it a popular choice for applications requiring clarity, such as packaging materials and consumer goods. The market is characterized by a competitive landscape with key players spread across different regions.
Key Trends and Drivers: Several key trends and drivers are expected to shape the GPPS market in the next five years:
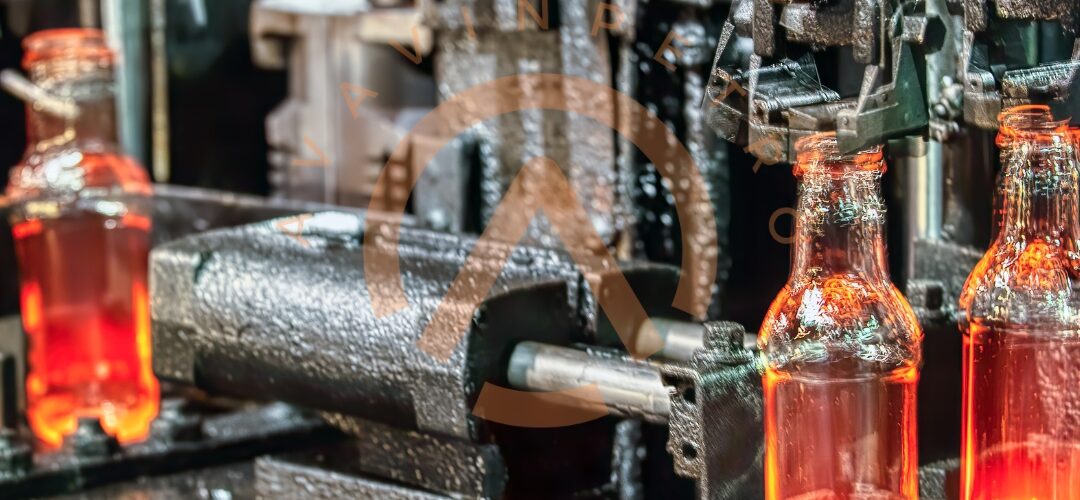
1. Growing Packaging Industry: The packaging industry, which represents a significant end-user sector for GPPS, is anticipated to experience steady growth. With increasing consumer demand for convenience and attractive packaging, GPPS is expected to find extensive usage in the production of food containers, trays, and disposable packaging materials.
2. Rising Demand in Electronics: The electronics sector is another key driver for the GPPS market. With the proliferation of electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and consumer electronics, there will be a continuous demand for GPPS in applications like housings, covers, and panels due to its electrical insulating properties and ease of customization.
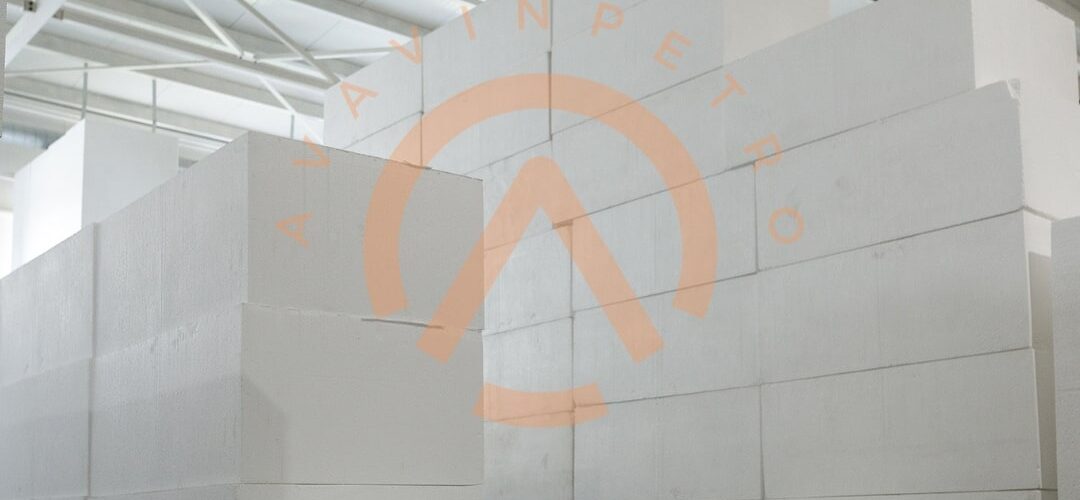
3. Construction and Building Industry: The construction and building industry is poised to contribute to the demand for GPPS in the coming years. GPPS is used in applications such as insulation, decorative moldings, lighting fixtures, and bathroom fittings due to its lightweight, thermal insulation, and aesthetic properties.
4. Sustainable Initiatives: Environmental concerns and regulatory policies are pushing manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices. The GPPS market is likely to witness an increased focus on developing bio-based and recyclable GPPS materials, catering to the growing demand for eco-friendly solutions.
Challenges and Opportunities: While the GPPS market presents promising opportunities, it also faces some challenges:
1. Increasing Competition: The GPPS market is highly competitive, with numerous players operating globally. Companies need to differentiate themselves by offering innovative products, enhancing their manufacturing processes, and providing value-added services to gain a competitive edge.
2. Shift Towards Alternatives: The growing demand for eco-friendly materials has led to a shift towards biodegradable and compostable alternatives to traditional plastics. GPPS manufacturers need to adapt and develop sustainable options to remain relevant and capture emerging opportunities.
Conclusion: The GPPS market is expected to witness positive growth in the next five years, driven by the expansion of the packaging, electronics, and construction industries. Companies that invest in research and development, focus on sustainable practices, and align with changing market demands will be well-positioned to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the evolving GPPS market.